Business process management (BPM) is an effective strategy for improving efficiency, streamlining operations, and achieving strategic goals. In this easy guide, we’ll explore what is business process management, its various types, essential process steps, templates, the wide-ranging benefits it delivers and more. Better understand, implement, and leverage the power of BPM to optimize your business operations. Let’s get started!
- What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
- What is a Business Process Management Strategy?
- Different Types of BPM
- Business Process Management Lifecycle
- Business Process Management Templates
- Why is BPM Important
- Business Process Management Best Practices
- Business Process Management vs Project Management
- Business Process Automation vs Business Process Management
- How to Use Creately to Manage Your Business Processes
What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
Business process management, or BPM for short, is a structured approach that organizations use to improve and optimize their operations. It serves as a set of guidelines and tools to systematically improve and streamline the way they conduct their business activities.
It involves analyzing, documenting, automating, and continuously refining these processes to improve efficiency, quality, and overall performance. BPM helps businesses align their operations with strategic goals and adapt to changing market conditions.
What’s particularly important about BPM is that it’s not a one-time effort; it’s a continuous cycle. Businesses employ it to make sure that they are consistently optimizing their processes.
What is a Business Process Management Strategy?
A BPM strategy is a plan that an organization creates to effectively manage and improve its business processes. It involves defining the goals and objectives related to process improvement, outlining the steps to achieve those goals, and specifying the tools, technologies, and methodologies to be used.
A well-defined BPM strategy acts as a roadmap for the organization to improve its operations, become more competitive, and adapt to changing business environments. It guides the entire BPM lifecycle from initial analysis to continuous improvement.
Different Types of BPM
There are several types of business process management, each with its own focus and purpose. Organizations can choose one or a combination of these BPM types based on their specific needs and the nature of their business processes. The goal is to align BPM with the organization’s goals and improve operational efficiency.
-
Process-centric BPM: This approach focuses on optimizing and managing individual business processes. It involves defining, modeling, and improving processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
-
Human-centric BPM: This BPM type emphasizes the role of people in processes. It focuses on how individuals interact with systems and each other to complete tasks, in order to improve their productivity and satisfaction.
-
Integration-centric BPM: This type of BPM concentrates on integrating different systems and applications within an organization to create seamless end-to-end processes. It’s especially useful in managing complex workflows and data exchange.
-
Document-centric BPM: This type is all about the handling and management of documents and content within business processes. It simplifies document creation, approval, storage, and retrieval.
Business Process Management Lifecycle
The BPM lifecycle refers to the stages involved in managing and improving business processes. It’s a continuous cycle aimed at achieving efficiency and effectiveness. The Business Process Management Life Cycle typically consists 5 stages as follow:
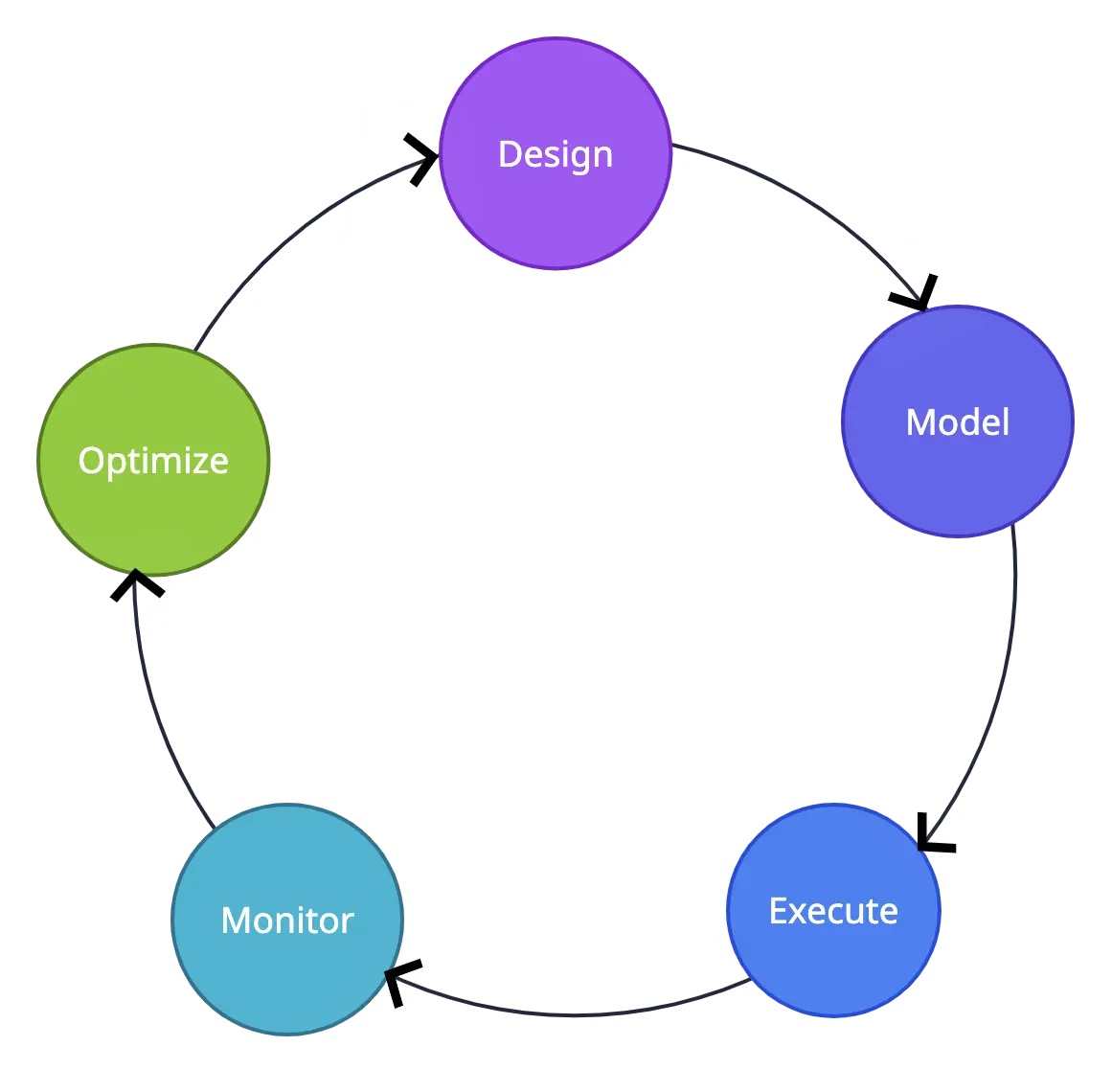
1. Design
In the “Design” phase of the BPM lifecycle, organizations begin by identifying the specific processes that require improvement. This phase involves carefully mapping out the current state of these processes, including how tasks are currently performed and who is responsible for each step. Make sure to set clear objectives for the process improvement effort, ensuring that these objectives align with the broader strategic goals of the organization.
2. Model
In this stage, create visual representations of the processes you want to improve. These representations can take the form of flowcharts, diagrams, or process maps.
The primary purpose is to visualize the structure and logic of the process. Stakeholders then analyze these models to identify potential bottlenecks, redundancies, or areas for improvements. Before implementing changes, organizations can use simulation tools to test various scenarios and analyze the impact.
3. Execute
This phase involves putting the designed and modeled processes into practice. You can do this manually, with employees following newly defined procedures, or with technology and automation tools. During this phase, employees need to be properly trained to make sure that they can execute the new processes correctly.
4. Monitor
Here organizations continuously monitor the performance of their processes. Key performance indicators (KPIs) and relevant metrics can be set up to measure process performance. To make sure the processes are working properly, collect and assess data regularly. You can also make use of advanced BPM systems which provide real-time monitoring capabilities, to intervene right away in case of delays or issues.
5. Optimize
During the “Optimize” phase, organizations analyze the data collected during the monitoring phase to identify areas for improvements. This analysis may include examining process efficiency, cycle times, error rates, and other relevant data. As a result, organizations make necessary changes to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their processes.
This could involve streamlining tasks, reducing bottlenecks, automating to eliminate manual work, or other improvements. Typically, the optimization phase leads back to the design phase, creating a feedback loop where insights from ongoing monitoring inform further process refinements.
Business Process Management Templates
BPM templates are pre-designed documents that can be customized to suit your specific BPM needs. Here are some examples of BPM templates that you can edit and use right away.
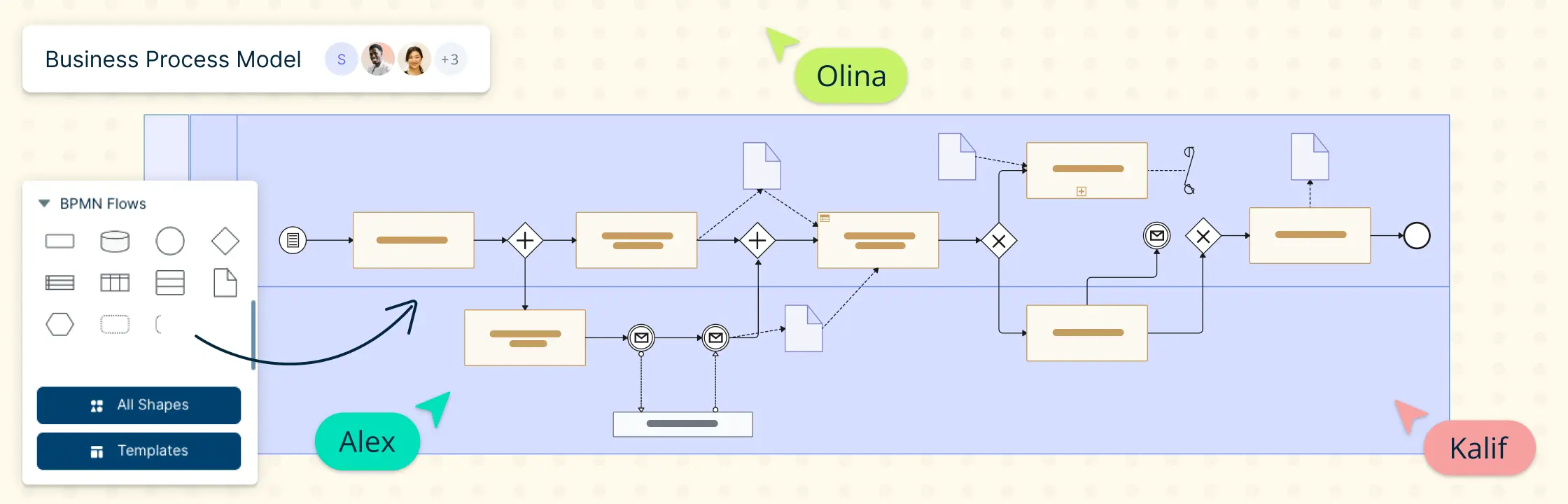
Business process modeling (BPMN)
Visual representations of how a process flows, often created using business process model and notation symbols.
Swimlane diagrams
Used to display the steps and decision points in a process, showing the flow of activities and responsibilities of different individuals or departments within the process.
Value stream maps
Value stream maps highlight the value-adding and non-value-adding steps within a process, helping to identify areas for improvement.
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Template
Standard operating procedures are predefined formats for documenting step-by-step instructions for performing tasks or processes.
Checklists
Simple lists of items or tasks that need to be completed as part of a process.
Root cause analysis templates
Tools such as fishbone diagrams or the “5 Whys” technique to identify the root causes of problems within a process.
Risk assessment template
Formats for evaluating and documenting potential risks associated with a process.
Why is BPM Important
Benefits of BPM contribute to overall organizational success and growth. Some of the benefits include;
-
Increased efficiency: Business process management helps organizations to streamline their processes, eliminating unnecessary steps and reducing errors. This leads to increased efficiency, cost savings, and quicker task completion.
-
Consistency and quality: It helps maintain consistent standards and quality in business operations. Standardized processes ensure that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations.
-
Adaptability: BPM helps organizations to be more agile and responsive to changing market conditions and customer needs. They can quickly adjust processes to stay competitive.
-
Visibility and control: BPM gives you a clear picture of how your processes are doing. It allows organizations to monitor progress, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions.
-
Compliance: Many industries have strict regulatory requirements. BPM helps make sure that processes comply with these regulations, reducing the risk of penalties and legal issues.
-
Cost savings: By optimizing processes, BPM can significantly reduce operational costs. It minimizes resource wastage, making operations more cost-effective.
-
Customer satisfaction: Efficient processes mean faster service delivery and higher customer satisfaction. Happy customers are more likely to remain loyal and recommend the business to others.
-
Risk management: BPM can identify potential risks in processes and help create strategies to mitigate them, reducing the likelihood of business disruptions.
Business Process Management Best Practices
Use these BPM best practices to create a structured approach to improving and managing business processes, helping organizations operate more efficiently and effectively over time.
-
Set clear goals: When you start any BPM effort, it’s essential to have a clear idea of what you want to achieve. Whether it’s making a process faster, reducing errors, or cutting costs, having specific goals helps keep everyone on the same page and motivated to improve.
-
Involve everyone: Processes often involve many people, from the ones who do the work to the managers who oversee it. By including everyone in the conversation, you benefit from their insights and expertise. They know the process inside out and might have valuable suggestions for making it better.
-
Write it down: Documenting a process means putting down on paper how it’s currently done. This can be in the form of flowcharts, diagrams, or written procedures. It makes the process clear and helps people understand it better, making it easier to identify areas for improvement.
-
Use the right tools: There are various software and tools available for managing processes, often referred to as BPM software. These tools can automate tasks, track progress, and provide a central place for everyone to work on the process.
-
Listen to feedback: People who work with the process might notice things that can be improved. Encouraging them to share their ideas and concerns creates a culture of improvement.
-
Train and manage change: When you make changes to a process, it’s important to teach everyone how to work with the new way of doing things. This training makes sure that everyone can use the improved process effectively. Additionally, managing change is about helping people adapt to the new way of working and addressing any concerns they might have.
-
Learn from data: The process data you collect gives valuable insights into what’s working and what’s not. It serves as a roadmap that shows you where to make improvements. Using this data, you can make informed decisions to improve the process continually.
Business Process Management vs Project Management
Business process management and project management serve different purposes in business operations. BPM focuses on improving ongoing, day-to-day processes that are important for the organization’s functioning, aiming to make them more efficient and effective continuously.
On the other hand, project management deals with handling specific, time-bound projects with defined goals and resources, which need to be completed within specified deadlines. In essence, BPM is about refining regular work, while project management is about achieving particular tasks with set objectives. To maintain operational excellence and accomplish project goals, organizations often use both approaches.
Business Process Automation vs Business Process Management
Business process automation and business process management are two related but different concepts. BPA is all about using technology to automate specific tasks within a process, like data entry or document processing, to make them faster and more accurate. In contrast, BPM is a broader approach focused on improving whole processes from start to finish. It considers everything in a process, including technology, people, and the way things are done. The goal of BPM is to make processes work better overall, making sure they’re efficient, effective, and aligned with an organization’s goals. Often, businesses use BPA to automate parts of their BPM efforts.
How to Use Creately to Manage Your Business Processes
Using an online visual collaboration and diagramming platform like Creately can help greatly improve your BPM efforts. Here’s how you can use Creately to improve BPM:
-
Process mapping: Start by creating visual representations of your processes. Creately offers extensive shape libraries and pre-made templates and tools to design flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, and process maps. This helps you document and communicate how processes work easily.
-
Collaborate with stakeholders: Creately is designed for teamwork. Collaborate with colleagues, process owners, and stakeholders in real-time with multi-user editing, synced previews, and commenting. They can provide insights, feedback, and suggestions, making it a collective effort.
-
Standardization: Use Creately to develop standard templates and guidelines for process documentation. This ensures consistency across your BPM initiatives.
-
Brainstorming: Conduct brainstorming sessions to identify process bottlenecks and improvement opportunities. Creately’s whiteboard capabilities, freehand drawing, visual brainstorming tools and sticky notes are useful for this. You can also use Creately’s Microsoft Teams integration to connect with participants and conduct the brainstorming session without leaving the meeting platform.
-
KPI tracking: Create visual dashboards and charts to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) related to your processes. Bring in data from external sources and visualize them on the canvas with meaningful shapes.
-
Collaborative documentation: Store all process documentation in one place within Creately with integrated notes. It serves as a central repository for process information, making it easily accessible for everyone involved.
Now that you know what is business process management, it’s time to put this knowledge into action. BPM is a key to making your organization work better, and it’s a journey of continuous improvement. By using BPM techniques and tools, you can streamline your processes, save time, and become more efficient.